Context and Sequentiality in Conversational Applications
Contextual memory in conversational applications plays a central role in any type of interaction between the Chatbot and the user. It is the bidirectional transfer of information where interlocutors are aware of the relational, environmental, and cultural context of the exchange. I will show some examples on how a contextual based system might improve the flow of the dialog.
- https://labs.hybris.com/2018/03/12/context-and-sequentiality-in-conversational-applications/ *
Consider the following sentence:
If you prefer salty food, tiramisù is a bad dessert to eat.
If we quote only the part that says:
tiramisù is a bad dessert to eat.
The resulting sense is completely misleading.
The speaker appears to simply saying that tiramisù is a bad dessert for everybody while it is a bad choice only for those who don’t like sweet and prefer instead salty food.
Even though the quoting is taken directly from the original sentence, it omits important informations that you need to have for understanding what the speaker is really saying. That omitted information is the context.
Context is the circumstances surroundings a message.
In the realm of conversational applications, where users can dialog with Chatbots, the context is a fundamental aspect for any type of interaction that spans from goal-oriented to one-shot tasks.
Let’s consider a simple case, where the same sentence appears in different contexts with consequentially different outcomes.
Taking the following sentence: Add bread into cart the system should react accordingly with what the user has previously entered, more precisely:
- If user has just searched for a product, the system will drive him to select the desired product and tap the button below → Drive the user to tap the related ‘Add to Cart’ button.
- In all other cases → Search for bread.
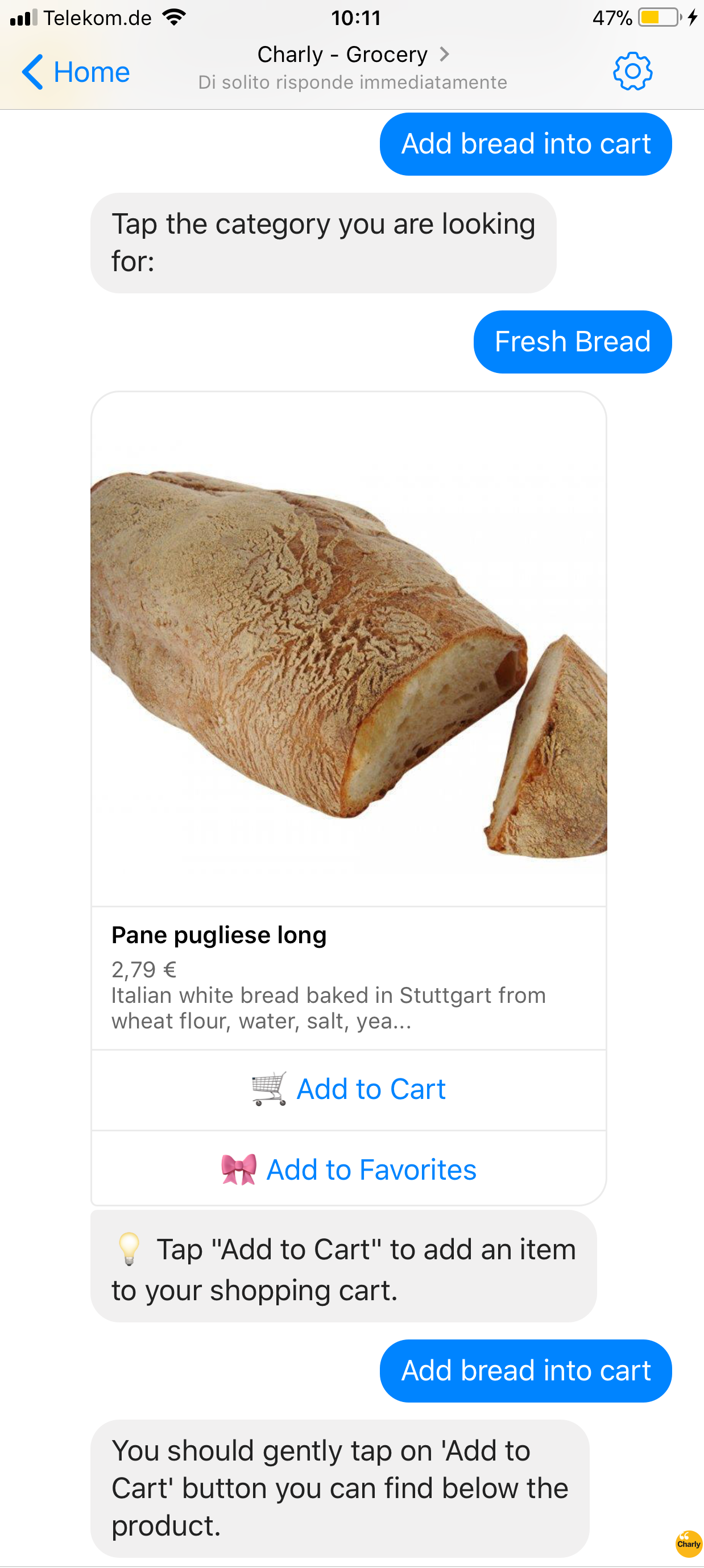
Context as customer engagement
The sequentiality of interaction between customer and Chatbot is the key for understand user’s intention, in any situation. In the online buying process, shortening the conversion rate and accelerating checkouts makes real difference between success and failure of e-commerce initiatives.
Conversational systems can tie customer engagement and purchase in a very short cycle. Smart sequencing, when seamlessly embedded in the processes, can lead new purchase opportunities.
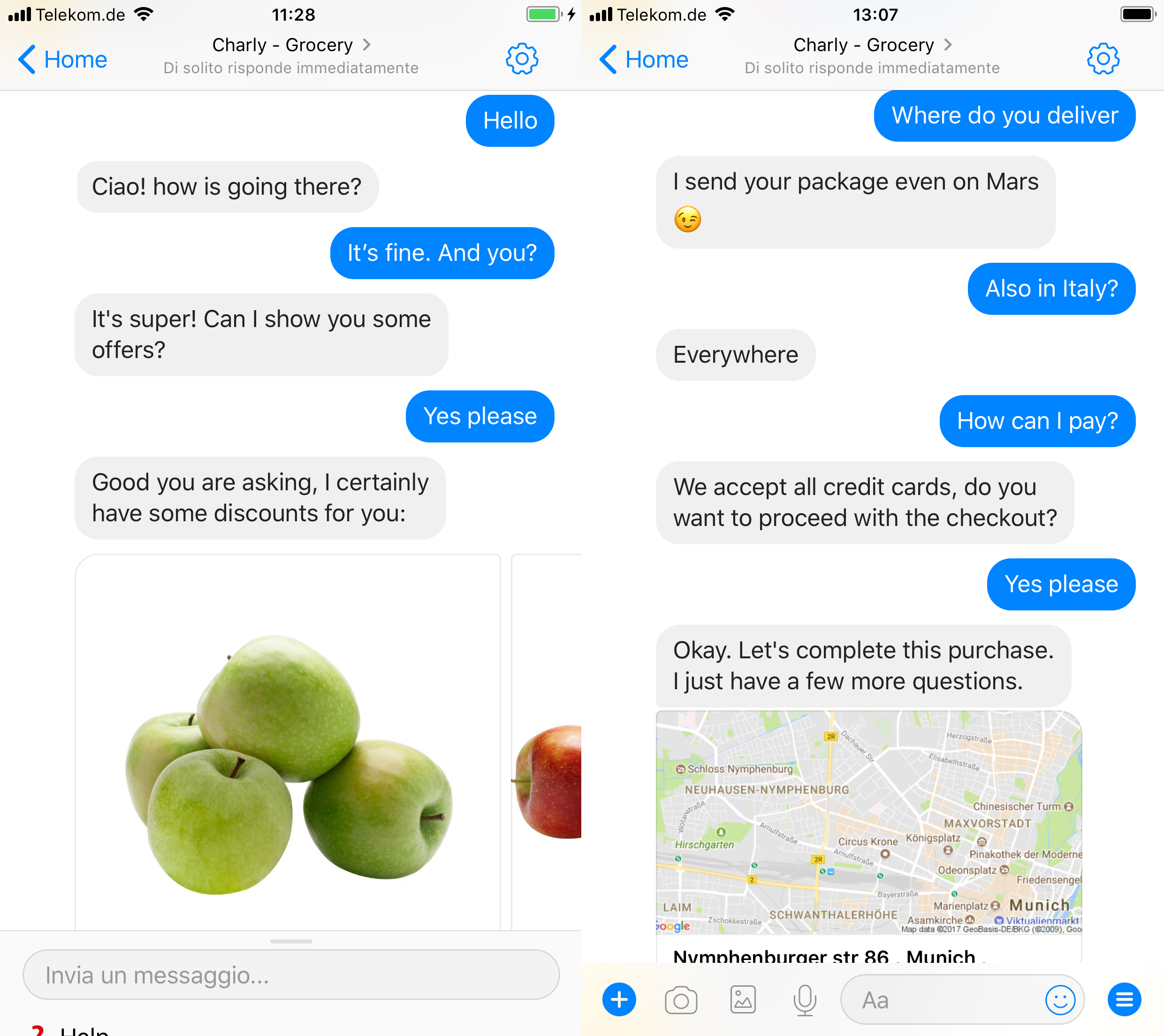
Exploring contextual repetition
Sequence is a collection of events that might contain repetition. Repetitive inputs might mean unsatisfied or not understood requests. In this odd example we can simulate a behavioral pattern where an interlocutor may get upset by an annoying and repetitive progression of unsolicited opinions, as may I rhetorically define this following conversation:
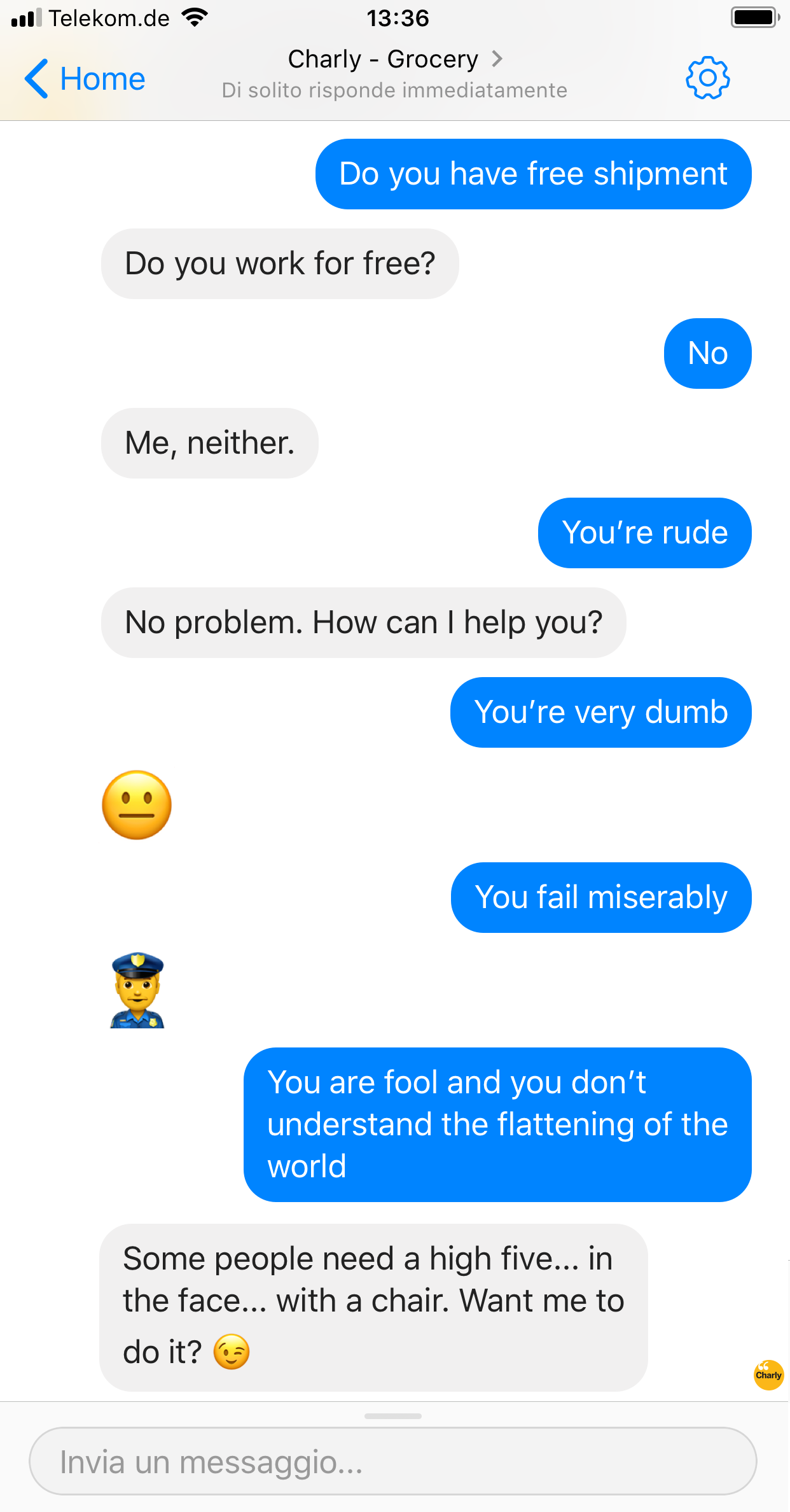
In this article I summarized how the ability to apply Contextual Intelligence should represent an intrinsic skill for any conversational application, for any scenario. It is the proficiency at automatically adapt responses to what the user is demanding during a conversation.
All those example cases are actually implemented in Charly. How I made it, will be the subject on a following article. Stay tuned!
Comments